The Power of Wind
Wind turbines harness the wind—a clean, free, and widely available renewable energy source—to generate electric power.
The animation below is interactive. You can start and stop the turbine’s movement, hover over parts to see their description, and use the icons in the lower right corner of the animation to switch views.
A wind turbine turns wind energy into electricity using the aerodynamic force from the rotor blades, which work like an airplane wing or helicopter rotor blade. When wind flows across the blade, the air pressure on one side of the blade decreases. The difference in air pressure across the two sides of the blade creates both lift and drag. The force of the lift is stronger than the drag and this causes the rotor to spin. The rotor connects to the generator, either directly (if it’s a direct drive turbine) or through a shaft and a series of gears (a gearbox) that speed up the rotation and allow for a physically smaller generator. This translation of aerodynamic force to the rotation of a generator creates electricity.
Wind turbines work on a simple principle: instead of using electricity to make wind—like a fan—wind turbines use wind to make electricity. Wind turns the propeller-like blades of a turbine around a rotor, which spins a generator, which creates electricity.
Explore a Wind Turbine
https://www.energy.gov/eere/wind/animation-how-wind-turbine-works
- The sun unevenly heating the atmosphere
- Irregularities of the earth's surface
- The rotation of the earth.
Wind flow patterns and speeds vary greatly across the United States and are modified by bodies of water, vegetation, and differences in terrain. Humans use this wind flow, or motion energy, for many purposes: sailing, flying a kite, and even generating electricity.
The terms "wind energy" and "wind power" both describe the process by which the wind is used to generate mechanical power or electricity. This mechanical power can be used for specific tasks (such as grinding grain or pumping water) or a generator can convert this mechanical power into electricity.
A wind turbine turns wind energy into electricity using the aerodynamic force from the rotor blades, which work like an airplane wing or helicopter rotor blade. When wind flows across the blade, the air pressure on one side of the blade decreases. The difference in air pressure across the two sides of the blade creates both lift and drag. The force of the lift is stronger than the drag and this causes the rotor to spin. The rotor connects to the generator, either directly (if it’s a direct drive turbine) or through a shaft and a series of gears (a gearbox) that speed up the rotation and allow for a physically smaller generator. This translation of aerodynamic force to rotation of a generator creates electricity.
https://www.energy.gov/eere/wind/how-do-wind-turbines-work
Types of Wind Turbines
The majority of wind turbines fall into two basic types:
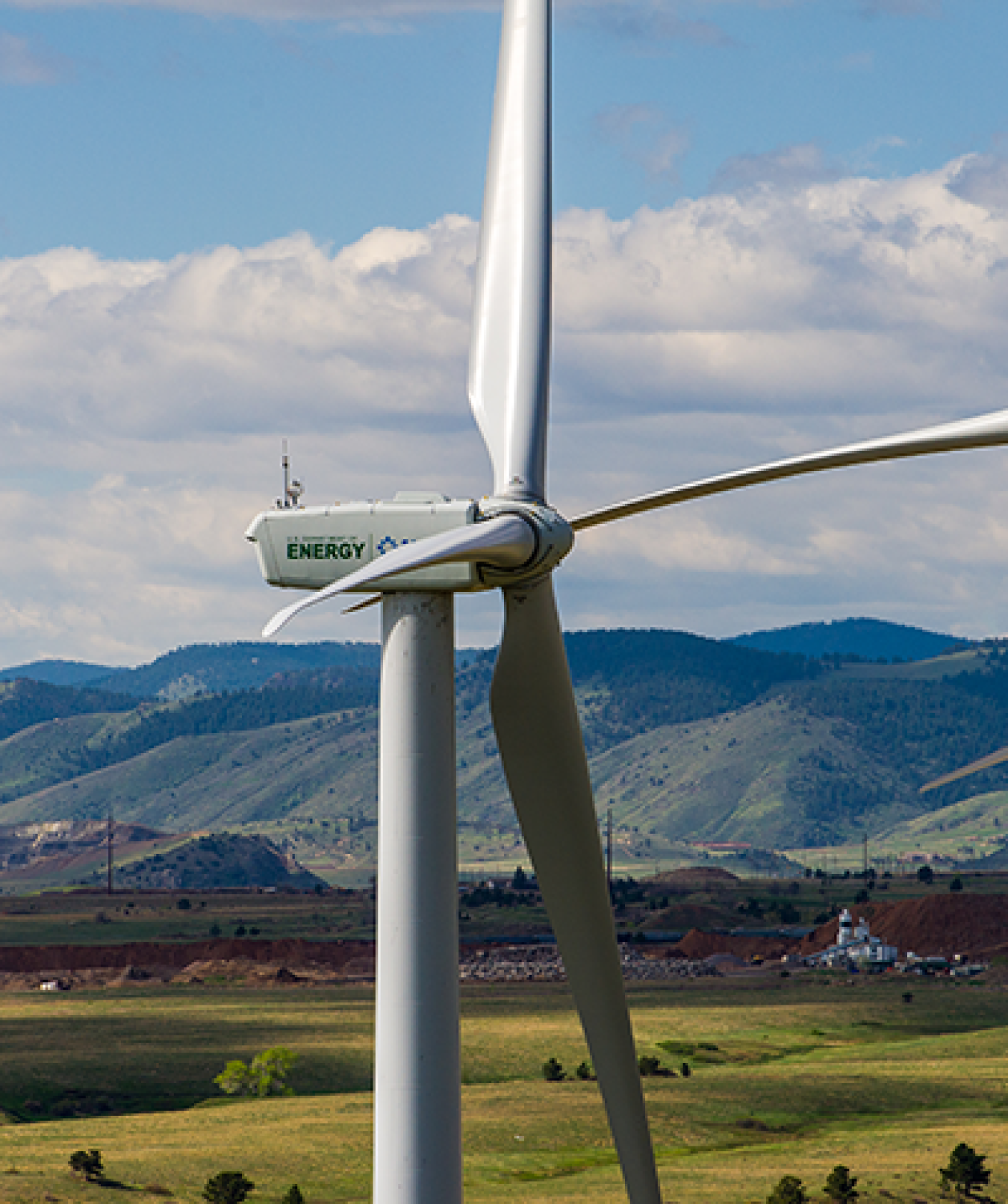
HORIZONTAL-AXIS TURBINES

Dennis Schroeder | NREL 25897
Horizontal-axis wind turbines are what many people picture when thinking of wind turbines.
Most commonly, they have three blades and operate "upwind," with the turbine pivoting at the top of the tower so the blades face into the wind.
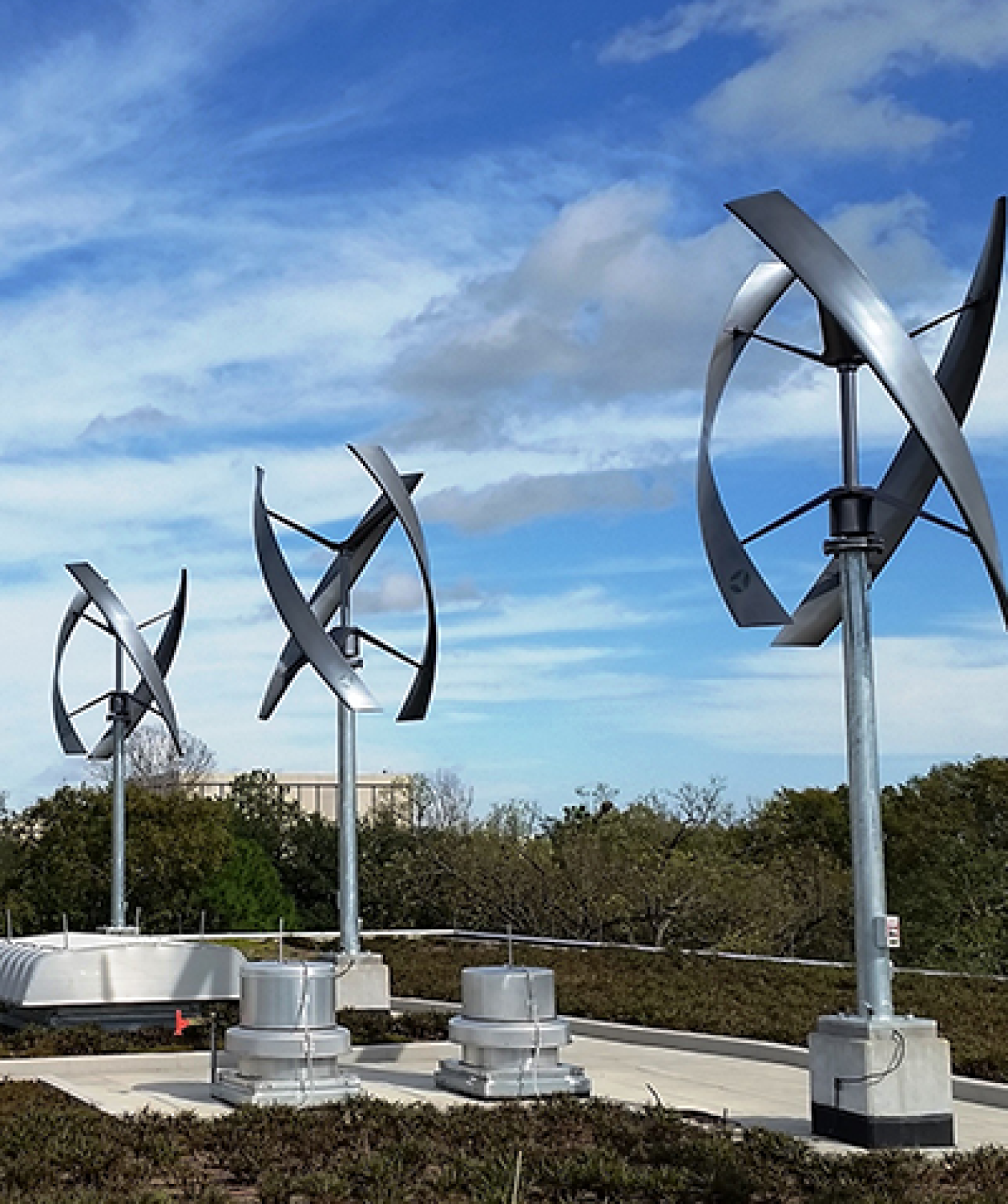
VERTICAL-AXIS TURBINES

Mike vanBavel | 42795
Vertical-axis wind turbines come in several varieties, including the eggbeater-style Darrieus model, named after its French inventor.
These turbines are omnidirectional, meaning they don’t need to be adjusted to point into the wind to operate.